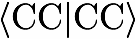
|
Main /
Calculation Of Vibrationally Averaged PropertiesVibrationally averaged properties can be computed within an anharmonic force-field calculation (keywords ANHARM=VIBROT, ANHARM=CUBIC, or ANHARM=QUARTIC, for details see the corresponding section on the calculation of anharmonic force fields) based on a Taylor expansion of the expectation value of the property of interest with respect to the normal coordinates. The corresponding formula for a property {$A$} is: {$ \langle A \rangle =A_e + \sum_r \frac{\partial A}{\partial Q_r} \langle Q_r \rangle + \frac{1}{2} \sum_{r,s} \frac{\partial^2 A}{\partial Q_r \partial Q_s} \langle Q_r Q_s \rangle + ... $} with {$\langle Q_r\rangle = - \frac{\hbar}{4 \omega_r^2} \sum_s \frac{k_{rss}}{\omega_s}$} and {$\langle Q_r Q_s \rangle = \delta_{rs} \frac{\hbar}{2\omega_r}$} with {$\omega_r$} as the corresponding harmonic vibrational frequency and {$k_{rss}$} as the cubic force constants in terms of normal coordinates. Computationally, this means that the cubic and semidiagoncal force fields need to be calculated as well as the corresponding property derivatives. The actual calculations thus consists of (a) a harmonic force-field calculation at the equilibrium geometry in order to get harmonic frequencies and the normal coordinates; The available properties are currently dipole moment (do not need additional calculations as already determined in the harmonic force-field calculation), polarizability tensor, NMR shielding tensors, nuclear spin-rotation tensors (as a byproduct in calculating vibrationally averaged NMR chemical shieldings), indirect spin-spin coupling constants, dipolar spin-spin coupling tensors, electric field-gradient tensors, quadrupole moment, magnetizability tensor and rotational g tensor. Input description for calculating vibrationally averaged properties Implementational details for calculating vibrationally averaged properties Examples for calculating vibrationally averaged properties Recommendations for calculating vibrationally averaged properties |