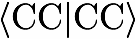
|
Main /
List Of Keywords In Alphabetical OrderA B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z specifies the way the {$\langle ab||cd\rangle$} molecular
orbital integrals are handled in post-MP2 calculations.
STANDARD (= 0) uses directly the corresponding MO integrals and thus results in an algorithm which in particular for large-scale calculations results in excessive use of disk space (storage of all
{$\langle ab||cd\rangle$} integrals. AOBASIS (=2) uses an AO-based algorithm to evaluate all
terms involving the {$\langle ab||cd\rangle$} integrals and significantly reduces the amount of
disk storage. ACTIVE_ORBI specifies the active orbitals used in a TCSCF calculation and has to be used in combination with the keyword CORE_ORBITALS. The active orbitals are specified by either NIRREP or 2*NIRREP integers specifying the number of active orbitals of each symmetry type, where NIRREP is the number of irreducible representations in the computational point group. If there are no orbitals of a particular symmetry type a zero must be entered. For more information and an example see the keyword OCCUPATION. ANHARMONIC specifies treatment of anharmonc effects by calculating
cubic and/or quartic force fields. ANHARM=VIBROT (=3) requests calculation of only those cubic constants of the form {$\phi_{nij}$}, where {$n$} is a totally symmetric coordinate. These are sufficient to determine the vibration-rotation interaction constants needed to calculate vibrational corrections to rotational constants, but are {\it not} sufficient to generate the corresponding cubic constants of isotopologues that have a lower point-group symmetry ({\it i.e.} HOD isotopologue of water). ANHARM=VPT2 (=1, note that the old keyword ANHARM=CUBIC can be still used and is equivalent to ANHARM=VPT2) generates all cubic constants and all quartic constants apart from those of the form {$\phi_{ijkl}$}, which is enough for: 1) generation of cubic constants of isotopologues (see manual entries associated with anharmonic calculations for an example); 2) calculation of vibrational energy levels with VPT2. This keyword also directs the program to analyze resonances and calculate intensities of one- and two-quantum transitions. ANHARM=FULLQUARTIC (=2) (not part of the public release) is largely self-explanatory; it directs the program to calculate all quartic constants. This is sufficient (but this has not been implemented) to generate the full quartic force field of all isotopologues. ANH_ALGORITHM specifies which algorithm is used for ANHARM=VIBROT, ANHARM=VPT2, and ANHARM=FULLQUARTIC
calculations. IF STANDARD (=0) is chosen, then simply invoking xcfour will
cause a complete job to be run with all second-derivative calculations being done in
series. If 'PARALLEL (=1), then the job stops after the second-derivative calculation
at the reference geometry and generates out all input geometries for the remaining calculation.
These can be then processed in 'parallel' (currently not recommended). ANH_POINTS specifies the number of points used for the numerical differentiation in the computation of cubic and quartic force constants based on analytically evaluated Hessians. 1 refers to the standard two-point formula, 2 refers to the four-point formula, etc. Default: 1 ANH_DERIVATIVES specifies whether the anharmonic force field is calculated using analytic gradients
(ANH_DERIVATIVES=FIRST) or analytic Hessians (ANH_DERIVATIVES=SECOND). ANH_STEPSIZE Controls the stepsize used in anharmonic force
field calculations. The value is specified in reduced normal coordinates,
which are dimensionless. The actual stepsize used in the calculation
is 10$^6$ the value specified(as an integer) in the ZMAT file. ANH_SYMMETRY Specifies whether nonabelian symmetry is to be
exploited in determining displacements for ANHARM=VIBROT or VPT2
calculations. If set to NONABELIAN (= 0), maximum advantage will be taken
of symmetry and the full set of cubic force constants will be generated
from a skeleton set by application of the totally symmetric projection
operator. If set to ABELIAN (= 1), only the operations of the abelian
subgroup will be exploited.\\
''It is important to point out that
the symmetrization currently works only for cubic constants.'' Therefore,
if you require quartic force constants (for frequency calculations),
you MUST use the ABELIAN option. Moreover, the latter work
for only asymmetric tops and linear molecules. AO_LADDERS Can be used to control the algorithm used by CFOUR when terms involving {$\langle ab||cd\rangle$} molecular orbital integrals are calculated in the atomic orbital basis (see keyword ABCDTYPE above). MULTIPASS (= 0) uses an approach where the AO integral file is read a number of times in order to ensure maximal vectorization and is usually the optimal strategy on supercomputers; SINGLEPASS (= 1) determines the contributions with only a single pass through the AO integrals, but at the cost of significantly reduced vectorization. In general, however, SINGLEPASS is definitely preferable on workstations with RISC architectures. (Default : MULTIPASS on all 64-bit machines (e.g., CRAY-YMP) ; SINGLEPASS on all 32-bit machines (e.g., IBM-RS6000, HP-735, SGI-Indigo, DEC alphastations)). SPARSE_AO (=2) uses a sparse matrix algorithm which first rearranges the integral matrix in order to get "well-occupied" and "very sparse" blocks. "Well-occupied" blocks will be multiplied by matrix multiplication while in "very sparse" blocks only the non-zero elements are considered. The computational time is further reduced using symmetrized and anti-symmetrized integral and amplitude matrices in the multiplication. Substantial saving is assumed if SPARSE_AO (=2) is used. AV_SCF ON (=1) requests and averaged SCF over two states. So far only implemented for degenerate dublett-Pi states and used in conjunction with SOPERT. specifies the AO basis used in the calculation. One can either specify a basis known to CFOUR or via BASIS=SPECIAL (=0) requests an arbitrary basis (see non-standard basis-set input). However, the latter must be available in the supplied GENBAS file. As standard basis sets, currently the following are available: STO-3G Default: SPECIAL BFIELD specifies whether the calculation is performed in the presence of a finite magnetic field (ON) or not (OFF). BREIT experimental use BRUCK_CONV specifies the convergence criterion in Brueckner based CC calculations. The calculation
is considered to be converged when the absolute value of largest single excitation amplitudes
falls below 10$^N$, where NNN is the value associated with the keyword. BRUECKNER specifies whether Brueckner orbitals are to be determined for the specified CC method.
OFF(=0) Brueckner orbitals are not to be determined, ON (=1) they are to be
determined. BUFFERSIZE experimental use defines the level of calculation to be performed. Available are: CACHE_RECS The number of records held in the i/o cache used by the post-SCF programs. The maximum number of records which can be held is 100.\\ Default : 10 CCORBOPT experimental use CC_CONV specifies the convergence criterion for the CC amplitude equations. The amplitudes are
considered to be converged when the maximum of all (absolute) changes in the amplitudes is less
than 10$^N$, where $N$ is the value associated with the keyword. CC_EXPORDER specifies the maximum number of expansion vectors used in the iterative subspace to enhance convergence
in the solution of the CC equations. CC_EXTRAPOLATION specifies the type of convergence acceleration used to solve the CC equations. RLE (=0) uses
the RLE methods of Purvis and Bartlett, DIIS (=1) uses the DIIS approach by Pulay, NOJACOBI (=2)
uses RLE with continuous extrapolation, OFF (=3) uses no convergence acceleration.
In general, DIIS provides the best results and is recommended, while OFF often results in
poor convergence and thus cannot be recommended. CC_MAXCYC specifies the maximum number of iterations in solving the CC amplitude equations. CC_PROGRAM specifies which CC program is used. The available options are VCC (=0), ECC (=1),
MRCC (=2), EXTERNAL (=3), NCC (=5), and SACC (=6) (not part of the public release).
The default for all calculations except CCSDT(Q), CCSDT[Q], and CCSDTQ is currently VCC which requests usage
of xvcc, but in many cases (e.g., for CCSD and CCSD(T)) ECC should be preferred due to
the better performance of xecc (available currently for CCSD, CCSD+T, CCSD(T), and closed-shell
CCSDT-n, CC3, and CCSDT). The option NCC requests usage of xncc for closed-shell CCSD(T), CCSDT,
CCSDT(Q), CCSDT[Q], and CCSDTQ single-point calculations. The option SACC requests the usage of xsacc for closed-shell CCSD/CCSD(T) and unitary group based spin-adapted open-shell CCSD/CCSD(T) single-point energy and first-order property calculations. Note: only the open-shell doublet case can be handled with this program. MRCC and External are intended for
CC programs outside the CFOUR suite, e.g., the general CC module mrcc written by M. Kállay (Budapest, Hungary). Note: Using the option ECC is not recommended for ROHF gradients. That is, if you are doing a geometry optimization with ROHF as your reference wave function then it is safe to use the option VCC. CHARGE specifies the molecular charge. CHOLESKY specifies whether Cholesky decomposition of two-electron integrals is used (ON) or not (OFF). CHOL_ALGORITHM specifies which algorithm is used for the Cholesky decomposition of two-electron integrals: (ORIGINAL) or (TWOSTEP). CHOL_TEST specifies whether the Cholesky decomposition is checked by reconstructing the original integrals (ON) or not (OFF). CIS_CONV specifies the convergence threshold (as {$10^{-N}$}) for CIS calculations. COMM_SIZE experimental use CONTINUUM signifies that one or more "continuum" orbitals should be added to the calculation. VIRTUAL and DVIRTUAL specify one or two orbital which should be initially unoccupied (in the SCF calculation), while OCCUPIED and DOCCUPIED specify one or two orbitals which should be initially occupied. CONTRACTION specifies the contraction scheme used by the integral and integral derivative program.
SEGMENTED (=0) uses a segmented contraction scheme; GENERAL(=1) uses a
general contraction scheme, and UNCONTRACTED(=2) uses the corresponding uncontracted sets. Note that even for truly segmented basis sets, the integral
programs run significantly faster in the GENERAL mode. CONVERGENCE specifies convergence criterion for geometry optimization. Job terminates when RMS gradient is below {$10^{-N}$} Hartree/bohr, where $N$ is the value specified by CONVERGENCE. (Value must be specified as an integer). COORDINATES specifies the type of coordinates used in the input file ZMAT. The keyword INTERNAL (=0)
means that the geometry is supplied in the usual Z-matrix format, while CARTESIAN (=1) means
that the geometry is given in Cartesian coordinates. A third option is XYZINT (=2) for which
a Z-matrix connectivity is defined, but with values of the internal coordinates defined implicitly by
supplying Cartesian coordinates. Note that geometry optimizations are currently only possible for
COORDINATES=INTERNAL and COORDINATES=XYZ2INT. CORE_ORBITALS specifies the core orbitals used in a TCSCF calculation and has to be used in combination with the keyword ACTIVE_ORBI. The core orbitals are specified by either NIRREP or 2*NIRREP integers specifying the number of core orbitals of each symmetry type, where NIRREP is the number of irreducible representations in the computational point group. If there are no orbitals of a particular symmetry type a zero must be entered. For more information and an example see the keyword OCCUPATION. CPCAS_CONV (not part of the public release) specifies the convergence criterion for the iterative solution of the CP-CASSCF equations. The solutions are considered
to be converged when the residual norm of the error vector falls below 10$^{-N}$. CPHF_CONVER specifies the convergence criterion for the iterative solution of the CPHF and Z-vector equations. The solutions are considered
to be converged when the residual norm of the error vector falls below 10$^N$. CPHF_MAXCYC specifies the maximum number of cycles allowed for the solution of the CPHF- and/or Z-vector equations. CURVILINEAR specifies whether or not Hessian matrix is transformed (nonlinearly) to curvilinear internal coordinates. A value of 0 (or OFF) turns the transformation off if the analytic force constants are not available, while it is always performed if CURVILINEAR=1 (or ON). Values higher than 1 (or NO) unconditionally turn the transformation off. specifies whether the diagonal Born-Oppenheimer correction (DBOC) to the energy is evaluated (ON =1) or
not (OFF =0). DBOC calculations are currently only available for HF-SCF and CCSD
using RHF or UHF reference functions. DCT specifies whether the Dipole Coupling Tensor (DCT) is calculated (ON =1) or
not (OFF =0). DERIV_LEVEL specifies whether or not energy derivatives are
to be calculated and if so whether first or second derivatives are computed.
ZERO (= 0) derivatives are not
calculated, FIRST (=1) first derivatives are calculated,
SECOND (=2) second derivatives are calculated. DIFF_TYPE specifies whether orbital-relaxed (RELAXED =0) or orbital-unrelaxed
(UNRELAXED =1) derivatives are computed in the CC calculation. DIRECT experimental use DIAG_MRCC experimental use DROPMO specifies which molecular orbitals will be dropped from
the post-SCF calculation. The orbitals are numbered in ascending order
from the most stable (negative energy) to the most unstable (largest
positive energy). Individual orbitals must be separated with a dash,
while x>y means orbitals x through y inclusive. For example,
the string 1>10-55-58>64, would result in
orbitals 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,55,58,59,60,61,62,63
and 64 being dropped. For UHF calculations,
the appropriate orbitals are deleted for both spin cases. No dropped
virtual MOs are currently allowed for gradient or property calculations. experimental use EA_SYM experimental use ECP specifies whether effective core potentials (pseudopotentials) are used (ON = 1)
or not (OFF = 0). EIGENVECTOR specifies which eigenvector of the totally symmetric
part of the block-factored Hessian is to be followed uphill in a
transition state search. Eigenvectors are indexed by their eigenvalues --
the lowest eigenvalue is 1, the next lowest is 2, etc. The default is
1, which should always be used if you are not looking for a specific
transition state which you know corresponds to motion along a different mode.
In the future, relatively sophisticated generation of a guessed eigenvector
will be implemented, but this is the way things are for now. Of course,
the value of EIGENVECTOR has no meaning if METHOD is not set to TS. EL_ANHARM experimental use, ON = 1 requests the evaluation of electrical anharmonicities. ESTATE_CONV specifies the threshold used in converging CC-LR/EOM-CC calculations.
The iterative diagonalization is continued until the RMS residual falls below {$10^{-N}$}
with N as the value specified with this keyword. EOM_NSING experimental use EOM_NTRIP experimental use EOM_NONIT controls whether non-iterative triples corrections are applied after various types of EOM-CCSD calculation. Works with EOMIP, might work with EOMEE, certainly doesn't work with EOMEA. Use with great caution, preferably after having a few drinks. Options are OFF and ON. EOM_NSTATES for experimental use only. Selects the iterative diagonalization algorithm for the EOMEE calculations.
If set to DAVIDSON, the general modified Davidson technique is used. If set to MULTIROOT, a multi-root Davidson approach is invoked that evaluates all roots of a symmetry block simultaneously. This approach is much more stable if the roots are energetically close to each other. EOM_PROPSTA EOMFOLLOW experimental use. ESTATE_DIAG experimental use. ESTATE_LOCK experimental use. ESTATE_MAXCYC The maximum number of expansion vectors used in the solution of EOMCC equations. ESTATE_PROP This keyword applies only to EOM-CC calculations and specifies whether any excited or ionized state one-electron properties are to be calculated. Proper use of this keyword requires a relatively advanced knowledge of quantum chemistry and the available options are discussed here. The options are : OFF (=0) [no properties or transition moments are calculated]; EXPECTATION (=1) [transition moments and dipole strengths are calculated along with selected one-electron properties which are evaluated as expectation values]; UNRELAXED (=2) [selected one-electron properties are calculated in an approximation that neglects relaxation of molecular orbitals]; RESPONSE (=3) [selected one-electron properties are calculated as analytic first derivatives of the energy]. Except for EOMCC calculations on two-electron systems (which are exact), properties obtained by the three approaches will not be equivalent. The default value for this keyword is slightly complicated. For TDA calculations, the default is EXPECTATION since the evaluation of transition moments involves only a negligible amount of additional computation relative to the evaluation of the excitation energies. For EOMCC, the default is OFF since evaluation of any transition moments or properties requires approximately twice the computational time. Transition moments and dipole strengths are evaluated by default for all values of ESTATE_PROP other than OFF. ESTATE_SYM specifies the number of excited states which are to
be determined in each irreducible representation of the computational
subgroup. The program attempts to find all of the lowest roots, but this
is not guaranteed because the eigenvalue problem is not solved by direct
matrix diagonalization, but rather by an iterative (modified Davidson)
algorithm. For excited state gradient calculations, only one
root (clearly) is used. In such a case, one and only one non-zero entry in
the string can be used, and this value is usually set to one (i.e.
ESTATE_SYM=0/1/0/0). (However sometimes one wants to calculate the gradient for,
say, the second root of a given symmetry, and in such a case, one could use
ESTATE_SYM=0/2/0/0. What happens is that both roots are calculated, but only the
second one is used in the subsequent density matrix and gradient calculation.)
The format used for this keyword is identical to that used in the OCCUPATION keyword, i.e. in the order A1/B1/B2/A2.
For example, for a computational subgroup having four symmetry species, the string
ESTATE_SYM=3/1/0/2 specifies that 6 total roots should be searched for, three in
the first block, one in the second block, and two in the fourth block. It is also
important to note that the %excite* input, if present, takes precedence over this
keyword, and the latter is ignored when an %excite* record is found in the ZMAT file. ESTATE_TRANS specifies whether just the excitation energies (OFF=0) or in addition
transition moments (EXPECTATION=1) are calculated. Note that this keyword should not be used in
excited-state calculations involving analytic gradients and that transition moments are essentially only available for EOM-CCSD/CCSD-LR. EVAL_HESS tells the program, in the course of a geometry optimization, to calculate the Hessian explicitly every N cycles. EXCITATION specifies in CC calculations using mrcc the excitation level if the calculation level
has been chosen as CC(n), CI(n), or CCn(n)''. EXCITE (to be replaced in the next release by EOM_METHOD) specifies the type of EOM-CC/LR-CC treatment to be performed. Available options are
NONE (=0), EOMEE (=3, the EOM-CC/CC-LR approach for the
treatment of excited states), EOMIP (=4, the EOM-CC/CC-LR approach for
the treatment of ionized states), EOMEA (=7, the EOM-CC/CC-LR approach for
the treatment of electron-attached states). EXTERN_POT allows the use of external pointcharges. Available options are OFF (=0), no pointcharges are considered, and ON (=1) pointcharges are read either from external file pcharges or from ZMAT as additional input section (%extern_pot*). The latter is considered first. Format: first row contains the number of pointcharges as integer, from second row the coordinates (Cartesian coordinates in bohr) and the charges (a.u.) are given. Note that SYMMETRY will be switched off, and the molecule will be treated in its original position (FIXGEOM=ON and no translation into the center of mass). Default: OFF Specifies the strength of a Fermi-Contact pertubation as required for finite-field calculations of spin densities and the FC contributions to indirect spin-spin coupling constants. The value must be specified as an integer and the FC strength used by the program will be the value of the keyword $x 10^{-6}$. The atom for which the FC perturbation is switched on is specified in the ZMAT file after the CFOUR command line and potential basis set input, as follows %spin density N with N as the number of atom (in (X5,I3) format) in the order they are written by JODA to the MOL file. Be aware that for some atoms, the calculation has to be run in lower symmetry or even without symmetry. FD_CALCTYPE specifies the algorithm used to compute the harmonic force constants in finite-difference
calculations.GRADONLY (=0) evaluates the force constants and dipole moment derivatives
by numerical differentiation of analytic gradients; ENERONLY (=1) evaluates the force
constants by second differences of energies (dipole moment derivatives are not evaluated);
while MIXED (=2) evaluates 1x1 blocks of symmetry-blocked force constants by second differences pf energies and all other elements by first differences of gradients. the GRADONLY and MIXED approaches may, of course, only be used hwen using computational methods for which analytic gradients are available. FD_IRREPS requests that only vibrational
frequencies of certain symmetry types are evaluated in a VIBRATION=FINDIF
calculation. The numbers of the
irreducible representations for which vibrational analysis is to be performed
are separated by slashes. For example, FD_IRREP=1/3/4 means compute
the frequencies of modes transforming as the first, third, and fourth
irreducible representations. If a symmetry is specified for which there are
no vibrational modes, the program will terminate. The labels of the
irreducible representations for this keyword are not usually the same as those
used in the rest of the calculation. Moreover, for some point groups,
for example, those of linear molecules, the two sets of labels refer to
different subgroups. There is as yet no straightforward way
to determine what they will be without starting a calculation. If one runs the
xjoda and then the xsymcor executables, the relevant irreducible representations
will be listed. If all vibrational frequencies are desired, this keyword need
not be included. FD_PROJECT specifies whether or not rotational degrees of freedoms are projected out from the symmetry-adapted coordinates
in a finite difference calculations. ON(=0) uses rotationally projected coordinates, while OFF(=1)
retains the rotational degrees of freedom. At a stationary point on the potential energy
surface, both options will give equivalent harmonic force fields, but
OFF should be used at non-stationary points. FD_STEPSIZE specifies the step length in mass-weighted coordinates (in 10**(-4) amu**0.5 bohr) used in generating
the force constant matrix by finite difference of Cartesian gradients. FD_USEGROUP In finite difference calculations using the FINDIF option, this keyword specifies the point group to be used in generating the symmetry-adapted vibrational coordinates. FULL (= 0) specifies the full molecular point group, COMP (= 1) specifies the Abelian subgroup used in the electronic structure calculation. FILE_RECSIZ This specifies the physical length (in integer words) of the records used in the word-addressable direct access files used by CFOUR. This value should always be chosen as a multiple of 512 bytes, as your local system manager certainly understands. FILE_STRIPE This option allows the splitting of files. Input is required in the form FILE_STRIPE=N1/N2/N43/N4/N5, where N1, N2, N3, N4, and N5 specify the number of files in which MOINTS, GAMLAM, MOABCD, DERINT, and DERGAM are splitted, respectively. FINITE_PERTURBATION specifies the field strength for a perturbation (defined
within a %perturbation section). The value must be given as an integer, and the field strength used by the program will be then the value of the keyword {$x10**(-6)$}. FIXGEOM specifies whether the geometry (given in terms of Cartesian coordinates) is reoriented (ON) or not (OFF). Note that the use of FIXGEOM=ON is not compatible with the exploitation of molecular point-group symmetry. FOCK This option is used to control the algorithm used for construction of the Fock matrix in SCF calculations. PK (= 0) uses the PK-supermatrix approach while AO (= 1) constructs the matrix directly from the basis function integrals. In general, PK is somewhat faster, but results in considerable use of disk space when out-of-core algorithms are required. FOCK=DIRECT (=2) requests an integral-direct calculation; this is currently only available with the integral package mint and not yet part of the public version. FREQ_ALGORIT experimental use. FROZEN_CORE specifies whether in the correlation treatment all electron (OFF =0) or only
the valence electrons (ON =1) are considered. This keyword provides an alternative
to the DROPMO keyword, as it allows frozen-core calculation without explicitly specifying
the corresponding inner-shell orbitals. FROZEN_VIRT specifies whether in the correlation treatment all virtual orbitals (OFF=0) or only
a subset of virtual orbitals (ON=1) are used. In the latter case, the threshold for
deleting virtual orbitals based on the orbital energey needs to be specified in a
%frozen_virt section. Used to control the handling and storage of two-particle density matrix elements with four virtual indices $\Gamma(abcd)$. DISK (=0) directs the program to calculate and store all elements of $\Gamma(abcd)$, while DIRECT (=1) tells the program to use alternative algorithms in which $\Gamma(abcd)$ is calculated and used ``on the fly''. Note that this option might be not available for all type of calculations. GAMMA_ABCI see GAMMA_ABCD. GENBAS_1 This keyword applies only to Hydrogen and Helium atoms and
specifies the number of contracted Gaussian functions per shell. There is
usually no need to use this keyword, but it can be useful for using a subset
of the functions in a particular entry in the GENBAS file, particularly for
generally contracted WMR basis sets. For example, if entry H:BASIS in the GENBAS
file contains 7 contracted s functions, 4 p functions and a single d
function, then setting GENBAS_1=730 would eliminate the last p function
and the d function. GENBAS_2 This keyword performs the same function as GENBAS_1 above,
but applies to second-row atoms. GENBAS_3 This keyword performs the same function as GENBAS_1 and
GENBAS_2, but applies to third-row atoms. GENBAS_4 This keyword performs the same function as GENBAS_1, GENBAS_2, and
GENBAS_3, but applies to fourth-row atoms. GEO_CONV specifies the convergence criterion for geometry optimization.
The optimization terminates when the RMS gradient is below {$10^{-N}$} Hartree/bohr, where
N is the specified value. GEO_MAXCYC specifies the maximum allowed number of geometry optimization cycles. GEO_MAXSTEP specifies largest step (in millbohr) which is allowed in geometry optimizations. GEO_METHOD specifies the used geometry optimization methods. The following values are
permitted: NR (=0) --- straightforward Newton-Raphson search for
minimum; RFA (=1) --- Rational Function Approximation search for
minimum (this method can be used to find minima when the initial
structure is in a region where the Hessian index is nonzero);
TS (=2) Cerjan-Miller eigenvector following search for a transition
state (can be started in a region where the Hessian index is not
equal to unity);
MANR (=3) --- Morse-adjusted Newton-Raphson search for minimum
(very efficient minimization scheme, particularly if the Hessian
is available); SINGLE_POINT (=5) for a single-point energy
calculation. ENERONLY (=6) requests a geometry optimization based
on single-point energy calculations. GIAO specifies whether gauge-including atomic orbitals (GIAOs, London atomic orbitals) are used (ON) or not (OFF). For the use of GIAOs in finite magnetic-field calculations specify GIAO=USE. GIMIC experimental use. GRID Keyword used to control type of grid calculation (see later section in this manual). Options are OFF (= 0), no grid calculation; CARTESIAN (= 1), steps are in Cartesian coordinates (which must be run with COORD=CARTESIAN); INTERNAL (= 2), steps are in Z-matrix internal coordinates; QUADRATURE (= 3) steps are chosen for an integration based on Gauss-Hermite quadrature. GRID_ALGO experimental use. GUESS Where the initial SCF eigenvectors are read from. MOREAD means to read from the disk (the `` JOBARC" file) and CORE means to use a core Hamiltonian initial guess. If MOREAD is chosen but no disk file is present, the core Hamiltonian is used. This keyword determines which action is taken by the linear response program. ON (= 1) the full effective Hamiltonian is calculated and written to disk; OFF (= 0) the ``lambda'' linear response equations are solved. HESS_TYPE experimental use. HFSTABILITY control analysis of the stability of RHF, ROHF and UHF wavefunctions,
as well as a possible search for a lower SCF solution. There are
three possible options for this keyword.
OFF (=0) does nothing, while ON (=1) performs a stability analysis and
returns the number of negative eigenvalues in the orbital rotation
Hessian. A third option, FOLLOW (=2) performs the stability analysis
and then proceeds to rotate the SCF orbitals in the direction of a
particular negative eigenvalue of the orbital rotation Hessian (see
the explanation of keyword ROT_EVEC), after which the SCF is
rerun. HF2_FILE experimental use. This keyword can be used to significantly reduce disk i/o, and should be implemented very soon. The following options are available: OFF (= 0), no special algorithms are used (the default case); ALL (=1) all quantities except the $\langle ab\vert\vert cd\rangle$ molecular integral lists are held in core; PARTIAL (= 2), the T2 and T1 vectors are held in core throughout the calculation; (=4) all quantities except the $\langle ab\vert\vert cd\rangle$ and $\langle ab\vert\vert ci\rangle$ integrals are held in core; (=5) $\langle ij\vert\vert kl\rangle$ and $\langle ij\vert\vert ka\rangle$ and two-index quantities are held in core; (=6) all direct access files (MOINTS, GAMLAM, etc.) are held in core. At present, these options have been implemented only in the energy code (xvcc) and the excitation energy code (xvee). INPUT_MRCC specifies whether an input for mrcc is written (ON,=0) or not (OFF,=1) if
CC_PROG=EXTERNAL has been specified. INTEGRALS This keyword defines what type of integral input will be written by JODA. VMOL (=1) or MINT (=0) have to be used with the programs of CFOUR. IRPSING This keyword is relevant for CC_PROGRAM=SACC and defines the symmetry (irreducible representation) of the singly occupied orbital in the reference state. For the closed-shell case, IRPSING=0. For SACC calculations involving open-shell doublet states, one could either use an ROHF reference state (REF=ROHF, MULT=2) or the RHF determinant of a closed-shell state obtained by adding an extra electron into the singly occupied orbital (REF=RHF, MULT=1). For both choices of the reference for a doublet state, IRPSING should be set to a nonzero value, viz., to the symmetry of the singly occupied orbital. Controls amount of debug printing performed by Joda. The higher the number, the more information is printed. Values of 25 or higher generally do not produce anything of interest to the general user. Do not set JODA_PRINT to 999 as this will cause the core vector to be dumped to disk. Dumps the keywords and their numerical designations. Default: OFF; Value must be specified as an integer. Convergence threshold for linear equations controlled by LINEQ_TYPE. Equations are iterated until smallest residual falls below {$10^{-N}$}, where N is the value associated with this keyword. LINEQ_EXPOR Maximum subspace dimension for linear equation solutions. LINEQ_TYPE Determines the algorithm used to solve linear equations ($\Lambda$ and derivative $T$ and $\Lambda$). POPLE (=0) uses Pople's method of successively orthogonalized basis vectors, while DIIS (=1) uses Pulay's DIIS method. The latter offers the practical advantage of requiring much less disk space, although it is not guaranteed to converge. Moreover, POPLE has not been tested for some time and should definitely be checked!\\ Default: DIIS LINEQ_MAXCY The maximum number of iterations in all linear CC equations. LINDEP_TOL The tolerance for basis set linear dependence. The basis set is considered linearly dependent and eigenvectors of the overlap matrix are neglected if the associated eigenvalues are less than {10$^{-N}$}.\\ Default: 8 LOCK_ORBOCC This keyword is used by the SCF program to determine if the orbital occupancy (by symmetry block) is allowed to change in the course of the calculation. ON (= 1) locks the occupation to that set by the keyword OCCUPATION [or the initial guess if OCCUPATION is omitted]; OFF (= 0) permits the occupation to change. LOC_TYP This keyword specifies the procedure used to determine localized orbitals (if requested) options are here PIPEK-MEZEY (=0) and FOSTER-BOYS (=1). LOC_CONV This keyword defines the convergence criterion for the orbital localization procedure. It sets the threshold for the maximum angle for orbital rotations to {$10^{-N}$} with N as the value specified. LMP2_TYP This keyword specifies the procedure used for the local MP2 treatment(if requrested). Specifies largest step (in millibohr) which is allowed in geometry optimizations. MEMORY_SIZE specifies the amount of core memory used in integer words (default) or in the units specified via the keyword MEM_UNIT. MEM_UNIT specifies the units in which the amount of requested core memory is given. Possible choices are INTEGERWORDS (default), kB, MB, GB, and TB. METHOD specifies the geometry optimization strategy. Four values are permitted: 0 (or NR) -- Straightforward Newton-Raphson search for minimum; 1 (or RFA) -- Rational Function Approximation search for minimum (this method can be used to find minima when the initial structure is in a region where the Hessian index is nonzero); 2 (or TS) Cerjan-Miller eigenvector following search for a transition state (can be started in a region where the Hessian index is not equal to unity); 3 (or MANR) -- Morse-adjusted Newton-Raphson search for minimum (very efficient minimization scheme, particularly if the Hessian is available); 4 is currently unavailable; 5 (or SINGLE_POINT) is a single point calculation. MRCC specifies the type of MRCC calculation. MK performs a MR-CC
calculation based on Mukherjee's ansatz. MULTIPLICITY specifies the spin multiplicity. Calculation of non-adiabatic coupling. In case of ON(=1) the method by Ichino, Gauss, Stanton is used to obtain the lambda coupling, while in case of LVC(=3) the lambda coupling is computed by means of the algorithm by Tajti and Szalay.
Furthermore, NACV(=2) requests the computation of the full non-adiabatic coupling. Note that for calculations using NACOUPLING=LVC or NACOUPLING=NACV options the multiroot diagonalization has to be used, as requested via the keyword EOM_NSTATES=MULTIROOT. NEGEVAL specifies what to do if negative eigenvalues
are encountered in the totally symmetric Hessian during an NR or
MANR geometry-optimization search. If NEGEVAL=ABORT (=0), the job will terminate
with an error message; if NEGEVAL=SWITCH (=1) the program will just
switch the eigenvalue to its absolute value and keep plugging away
(this is strongly discouraged!); and if NEGEVAL=-> RFA (=2), the keyword
GEO_METHOD
is switched to RFA internally and the optimization is continued. NEWNORM all components of spherical AO’s are normalized to 1. This feature can help with numerical convergence issues if AO integrals are involved. Currently only working for single-point energy calculations. NONHF specifies whether the reference function used in the correlation energy calculation satisfies the (spin-orbital) HF equations or not.
Usually there is no need to set this parameter (OFF = 0 and ON =1), since standard non-HF reference functions (QRHF and ROHF) set this flag automatically. NTOP_TAMP specifies how many t amplitudes will be printed for each spin case and excitation level. =N The largest N amplitudes for each spin case and excitation level will be printed. (Default : 15). NUC_MODEL (developer's version only) specifies which model is used for the nuclei. Defaults is the point-nucleus model (POINT = 0) which is also recommended
for all nonrelativistic calculations. For relativistic calculations, however, the use of a finite nucleus model (FINITE =1)
is recommended. Currently available is a Gaussian model. NUM_INST (not part of the public release) specifies how many eigenvalues of the RHF->UHF instability Hessian to look for. Only relevant for DQCSCF in conjunction with the keyword HFSTABILITY=2. specifies the orbital occupancy
of the reference function in terms of the occupation numbers of the orbitals and
their irreducible representations. The occupancy is specified by
either NIRREP or 2*NIRREP integers specifying the number of occupied
orbitals of each symmetry type, where NIRREP is the number of irreducible representations
in the computational point group. If there are no orbitals of a
particular symmetry type a zero must be entered. If the reference function is for an open-shell
system, two strings of NIRREP occupation numbers
separated by a slash are input for the
α and β sets of orbitals. OPEN-SHELL specifies which kind of open-shell CC treatment is
employed. The default is a spin-orbital CC treatment (SPIN-ORBITAL =1)
which is the only possible choice for UHF-CC schemes anyways.
For ROHF-CC treatments, the possible options are beside the
standard spin-orbital scheme a spin-restricted CC approach
(SR-CC=3), as well as a corresponding linear
approximation (which in the literature usually is referred to
as partially-spin-adapted
CC scheme) (PSA-CC=1). SR-CC and PSA-CC are within the CCSD approximation
restricted to excitations defined by the first-order interacting space
arguments. With the keywords PSA-CC_FULL(=2) or SR-CC_FULL(=6) inclusion of the so called "pseudo-triples" beyond the first-order interacting space is
also possible. OPT_MAXCYC specifies the maximum allowed number of geometry optimization cycles. ORBITALS specifies the type of molecular orbitals used in post-HF calculations. STANDARD (=0) requests
usage of the orbitals (from a corresponding HF-SCF calculation) without any modification. These
are in the case of RHF/UHF the usual canonical HF orbitals and in the case of ROHF calculations
the standard ROHF-orbitals with equal spatial parts for both the {\alpha$} and the {$\beta$} spin orbitals.
SEMICANONICAL (=1) forces in ROHF type calculations a transformation to so-called
semicanonical orbitals which diagonalize the occupied-occupied and virtual-virtual blockes
of the usual Fock-matrices. The use of semicanonical orbitals is, for example, required for
ROHF-CCSD(T) calculations and for those calculations also automatically set. LOCAL requests
a localization of the HF orbitals and this is currently done according to the Pipek-Mezey
localization criterion. experimental use. PARA_PRINT experimental use. PARA_INT experimental use. PERT_ORB specifies the type of perturbed orbitals used in energy derivative calculations.
STANDARD means that the gradient
formulation assumes that the
perturbed orbitals are not those in which the (perturbed) Fock matrix is diagonal.
CANONICAL means that the perturbed orbitals are assumed to be canonical.
This keyword is set automatically to CANONICAL in derivative calculations with
methods which include triple excitations (MBPT[4]/MP4, CCSD+T[CCSD],
CCSD[T], QCISD[T] and all iterative schemes like CCSDT-n and CC3) apart from CCSDT.
IJ_CANONICAL requests a canonical perturbed-orbital treatment
only for the occupied-occupied block of the unperturbed density matrix
in analytic derivative calculations. PNO_USE specifies whether pair natural orbitals (PNOs) are used in a local MP2 treament. The options are OFF (=1) and ON (=2). PNO_THRESHOLD specifies the cutoff for the selection of PNOs are used in a local MP2 treament.\\ Default: 7 POINTS specifies either single (=1, or SINGLE) or double (=2, DOUBLE) sided numerical differentiation in the finite difference evaluation of the Hessian. Two-sided numerical differentiation is considerably more accurate than the single-sided method and its use is strongly recommended for production work. PRINT controls the amount of printing in the energy and energy derivative calculation programs. Using a value of 1 will produce a modest amount of additional output over the default value of 0, which includes some useful information such as SCF eigenvectors, Fock matrix elements, etc. PROPS specifies whether and which molecular property is calculated. OFF(=0) means that
no property is calculated, FIRST_ORDER (=1) requests computation of various
one-electron first-order properties (e.g., dipole moment, quadrupole moment, electric field
gradient, spin densities,etc.), SECOND_ORDER (=2, in the next release replaced by STAT_POL)
computes static electric polarizabilities, DYNAMICAL (=7, in the next release replaced by
DYN_POL) requests the calculation of frequency-dependent polarizabilities (note that here an
additional input of the frequency is required), NMR (=5) requests the calculation of NMR
chemical shifts/chemical shielding tensors (by default using GIAOs), J_FC requests the calculation
of the Fermi-Contact contribution to indirect spin-spin coupling constants, J_SD the calculation of the
corresponding spin-dipole contribution, and J_SO the calculation of the corresponding spin-orbit
contribution to J; HYPERPOL (=22) invokes a calculation of static hyperpolarizabilities, DYN_HYP (=23) requests the calculation of frequency-dependent hyperpolarizabilities, SHG (=24) the calculation of hyperpolarizabilities related to
the second-harmonic generation,OPT_REC (=25) the computation of
hyperpolarizabilities related to optical rectification,
VERDET (=26) the calculation of Verdet constants. PROP_INTEGRAL allows storage of property integrals computed in xvdint on internal files (e.g., MOINTS
and GAMLAM, default choice INTERNAL (=0)) or on external files (EXTERNAL, =1). PSI ??? Specify which algorithm to use for QCSCF. Options are "FLM" (0) for the Flectcher-Levenberg-Marquardt optimization, which is the default, and "AH" (1) for a more standard Augmented Hessian optimization. AH is more efficient than FLM, however, FLM is guaranteed to converge. QC_MAXCYC Specify the maximum number of cycles in a QCSCF calculations. QC_MAXSCFCYC Specify the maximum number of standard SCF cycles before the QCSCF optimizazion. This preliminary iterations are used to determine the occupation number (which should therefore always be double checked, or provided from input). QC_NOISE (not part of the public release) Specify whether to add a random perturbation to the MO rotation gradient at the beginning of the second-order optimization. This can be useful to break an unwanted symmetry and is only relevant for DQCSCF. QC_RTRUST Trust radius for the second-order SCF optimization. Integer, the actual trust radius is QC_RTRUST/1000. The default (0) corresponds to a trust radius of 0.66 for RHF and ROHF (not part of the public release) and 0.25 for UHF. The defaults are reasonable for most cases, consider reducing them only for very, very hard convergence problems. QC_START Specify the convergence threshold for the preliminary SCF iterations before switching to quadratically convergent ones. Default is -1, as 10^(-(-1)) for the RMS variation of the density matrix and 10^0 for the Max variation. QM/MM specifies whether a QM/MM computation (ON) is carried out or not (OFF). QRHF_GENERAL The presence of this keyword specifies that a QRHF based CC calculation, or alternatively, an SCF calculation that uses the QRHFGUES option, is to be performed. QRHFGUES If this keyword is set to ON (=1), then the QRHF orbitals specified by the QRHF_GENERAL, QRHF_ORBITAL and QRHF_SPIN keywords are used as a starting guess for a restarted SCF procedure. This can be an extremely useful way to converge "difficult" SCF solutions, such as those that correspond to states that are not the lowest states of a given symmetry. Note that when this option is used, the calculation that is performed is not a QRHF-CC calcualtion; it is instead a UHF-based or ROHF-based calculation, depending on what type of reference is specified by the REFERENCE keyword. The QRHF aspect of the calculation is used simply as a device to converge the orbitals. QRHF_MINUS No longer used; antiquated way of specifying QRHF occupation changes. QRHF_ORBITAL By default, in QRHF calculations, electrons are removed from the highest occupied orbital in a symmetry block (symmetry block HOMO), while electrons are added to the lowest unoccupied orbital within a symmetry block (symmetry block LUMO). The purpose of the QRHF_ORBITAL keyword is to allow additional flexibility in choosing which orbitals will have their occupation numbers altered. The value of this keyword gives the offset with respect to the default orbital for the orbital which will be depopulated (or populated) in QRHF-CC calculations. For calculations involving more than one removal or addition of electrons, values are separated by commas and correspond to the QRHF_GENERAL input on a one-to-one basis. For example, specifying QRHF_GENERAL=2/-4,QRHF_ORBITAL=3/2 means that an electron will be added to the third lowest virtual in symmetry block 2 and another will be removed from the second highest occupied orbital in symmetry block 4. Examples given later in this manual further illustrate the QRHF input options and may help to clarify any confusion resulting from this documentation.\\ Default: 1 QRHF_PLUS No longer used; antiquated way of specifying QRHF occupation changes. QRHF_SPIN specifies the spin of the electrons modified by the QRHF_GENERAL and QRHF_ORBITAL keywords, where a value of 1 means alpha spin, while 2 corresponds to a beta electron. By default, electrons that are removed are assigned to beta spin, while added electrons are alpha. Note that this option allows one to construct low-spin determinants, which generally are unsuitable for single-reference coupled-cluster calculations. An important exception is the open-shell singlet coupled-cluster method (see keyword OPEN-SHELL=TD-CC above). ON (=1) requests a calculation of Raman intensities based on the geometrical derivatives of the static polarizability tensor, while DYN (=2) requests a calculation of Raman intensities based on the derivatives of the dynamical polarizability tensor. RAMAN_ORB specifies whether Raman intensities are calculated
with orbital relaxation with respect to the electric
field perturbation (RELAXED, = 1) or without
orbital relaxation (UNRELAXED, = 0). RDO specifies whether or not relaxed density natural orbitals are to be computed. This option only has meaning for a correlated calculation. =0 Do not compute, =1 compute.\\ Default: 1 REFERENCE specifies the type of SCF calculation to be performed.
RHF (= 0) requests a restricted Hartree-Fock reference; UHF (= 1) an unrestricted
Hartree-Fock reference; ROHF (= 2) a restricted open-shell Hartree-
Fock calculation; TCSCF (=3) a two-configurational SCF calculation,
and CASSCF (=4) a complete-active
space SCF calculations (currently not implemented). RELATIVISTIC specifies the treatment of relativistic effects. The default is a non-relativistic treatment (OFF), while
perturbational treatments
are invoked via MVD1 (mass-velocity and 1-electron Darwin conribution), MVD2 (mass-velocity and 1- and 2-electron
Darwin contribution), DPT2 (second-order direct perturbation theory approach), SF-DPT4 (scalar-relativistic part of
fourth-order direct perturbation theory, DPT4 (full fourth-order DPT including spin-orbit corrections), SF-DPT6 (scalar-relativistic part
of sixth-order direct perturbation theory), DPT2-1E (one-electron variant of DPT2), SFREE (spin-free
treatment), X2C1E (spin-free X2C-1e treatment), X2CMF (spin-free X2C treatment based on spin-free Dirac-Coulomb orbitals), or DPT (synonym with DPT2). RELAX_DENS specifies whether the relaxed density matrix is computed for correlated wave functions. OFF (= 0) The relaxed density will not be computed, ON (= 1) it will be computed. (Default : 0). RES_RAMAN this option can be used to convert an analytically calculated gradient vector to a particular normal coordinate representation. A useful application is to calculate the gradient of an electronically excited state in the normal coordinate representation of the ground electronic state, as this provides a first approximation to resonance Raman intensities (hence the name of the keyword). Calculations that use the RESRAMAN option require the externally supplied force constant matrix FCMFINAL, which is written to disk during the course of both analytic and finite-difference vibrational frequency calculations. No such transformation is performed if OFF (=0); while ON (=1) directs the program to evaluate the gradient and transform it to the chosen set of normal coordinates. A warning message is printed if the force constant matrix is unavailable.\\ Default: OFF RESET_FLAGS experimental use. RESTART_CC offers the possibilty to restart a CC calculation which stopped for various reasons, e.g. time limit, in the correlation part. However, note that a restart which is specified by ON (= 1) needs the following files of the previous unfinished calculation: JOBARC, JAINDX, MOINTS, and MOABCD. ROT_EVEC specifies which eigenvector of the orbital
rotation Hessian is to be used to rotate the original SCF orbitals. By
default, it will use that associated with the lowest eigenvalue of the
totally symmetric part of the block-factored Hessian, as this choice often
leads to the lowest energy SCF solution. For RHF stability checks, only
those instabilities which correspond to RHF solutions will be considered.
It is important to understand that following non-symmetric eigenvectors
lowers the symmetry of the wavefunction and that following
RHF --> UHF stabilities leads to a UHF solution.
To converge the SCF roots associated with such instabilities, one must
run the calculation in reduced symmetry and as a closed-shell UHF
case, respectively. ROT_EVEC=n directs the program to follow the vector
associated with the nth lowest eigenvalue having the proper symmetry
(totally symmetric) and spin (RHF-->RHF or UHF-->UHF)
properties. relevant if CC_PROGRAM=SACC and specifies the type of the spin-adapted open-shell CC ansatz for the doublet case. COS-CC (= 0): employs the combinatoric open-shell CC ansatz or NORMAL (= 1): uses a normal-ordered exponential ansatz without contractions among cluster amplitudes. Note: this keyword is important only for the open-shell doublet case, it is a dummy otherwise. SACC_CALC relevant if CC_PROGRAM=SACC and defines the type or the stage of the SACC calculation. DENSITY (= 0): calculates single-point energy if DERIV_LEVEL and PROPS are set to their respective default values, i.e., ZERO and OFF. Choosing SACC_CALC=DENSITY in addition computes one-particle charge and spin density matrices using the SACC program if DERIV_LEVEL=FIRST and PROPS=FIRST_ORDER. The other option for SACC_CALC is PROPERTIES (= 1), which computes first-order one-electron properties, e.g., dipole moments, quadrupole moments, charge and spin densities at nuclei, the electric-field gradient tensor, etc. For computing first-order properties using the SACC program, two consecutive runs are necessary: the first one using SACC_CALC=DENSITY, DERIV_LEVEL=FIRST, PROPS=FIRST_ORDER, and the second run using SACC_CALC=PROPERTIES, DERIV_LEVEL=FIRST and PROPS=FIRST_ORDER. The SACC_CALC=DENSITY run for a doublet state:
The SACC_CALC=PROPERTIES run for a doublet state:
For closed-shell molecules, the QRHF keywords are to be omitted altogether. SACC_ORBS relevant if CC_PROGRAM=SACC and specifies the type of orbitals to be used for SACC calculations. STANDARD (= 0): standard ROHF or RHF orbitals are employed or SEMICANSP (= 1): spatial semicanonical orbitals generated from standard ROHF orbitals are employed. Using SACC_ORBS=SEMICANSP is mandatory only in one situation: if REF=ROHF, MULT=2, CALC_LEVEL=CCSD(T), and SACC_CALC=DENSITY. For all other cases, SACC_ORBS=STANDARD should be chosen. Note: The SACC program does not use the ORBITALS keyword. Therefore, ORBITALS may be set to STANDARD (default) if CC_PROGRAM=SACC. The program sets this anyway. SACC_PROP relevant for the case CC_PROGRAM=SACC and specifies whether orbital-relaxed (RELAXED = 0) or unrelaxed (UNRELAXED = 1) properties will be computed using the SACC program. Note: if CC_PROGRAM=SACC, then DIFF_TYPE=UNRELAXED should be used. This is because the SACC program uses its own inbuilt implementation for orbital response treatment. SAVE_INTS tells CFOUR whether to delete large files (AO integrals and MOINTS file for now) when they are no longer needed. OFF (= 0) They will not be saved, ON (= 1) they will be saved. SCALE_ON controls whether step scaling is based on the absolute step length (1-norm) (=0 or MAG(S)) or the largest individual step in the internal coordinate space (=1 or MAX(S)).\\ Default: MAG(S). SCF_CONV specifies the convergence criterion for the HF-SCF equations.
Equations are considered converged when the maximum change in
density matrix elements is less than 10$^{-N}$. SCF_DAMPING controls the damping (in the first iterations
(specified by SCF_EXPSTART via
D(new) = D(old) + X/1000 * [D(new) - D(old)] with X as the value
specified by the keyword. The default value is currently 1000 (no damping),
but a value of 500 is recommended in particular for transition metal
compounds where the SCF convergence is often troublesome. SCF_EXPORDER specifies the number (N) of density matrices to be used
in the DIIS convergence acceleration procedure. SCF_EXPSTART specifies the first iteration in which the DIIS
convergence acceleration procedure is applied. SCF_EXTRAPOLATION specifies whether or not the DIIS extrapolation is used to accelerate convergence of the SCF procedure. OFF (=0): do not use DIIS, ON (=1= use DIIS.\\ Default : ON. SCF_MAXCYC specifies the maximum number of SCF iterations. SCF_PRINT This keyword is no longer in use. SCF_PROG Specifies whether to use the standard or the quadratically convergent SCF code. Options are "SCF" (0), "QCSCF" (1), and "DQCSCF" (2). "DQCSCF" is not part of the public release. Default : """0""" SD_FIELD specifies the strength of a spin-dipole pertubation as required for finite-field calculations of the SD contributions to indirect spin-spin coupling constants. The value must be specified as an integer and the SD strength used by the program will be the value of the keyword $x 10^{-6}$. (Default : 0, currently not implemented) SOPERT Default : OFF. Perturbative treatment of spin-orbit splittings in dublett-pi states via multireference coupled-cluster theory. MKMRCC (=1) requests a treatment based on Mukherjee's multireference coupled-cluster theory.EMRCCSO (=2) requests the expectation value of a similarity transformed spin-orbit operator. Please note that symmetric orbitals are needed, e.g., using AV_SCF. For more information on the theory see J. Chem. Phys. 136, 111103 (2012). SPHERICAL specifies whether spherical harmonic
(5d, 7f, 9g, etc.) or Cartesian (6d, 10f, 15g, etc.) basis functions
are to be used. ON (= 1) uses spherical harmonics, OFF (= 0) uses
Cartesians. SPIN_FLIP controls whether excitation energy calculations allow for a ``spin flip'' which changes the $M_s$ quantum number. Such calculations have some advantages for biradicals and are currently implemented (together with gradients) for CIS and CIS(D) calculations. Options are OFF and ON.\\ Default : OFF. SPIN_ORBIT Experimental Use! ON (=1) requests calculation of one-electron spin-orbit integrals. SOMF (=4) provides a mean-field treatment of the two-electron terms, and SA-SOMF (=2) provides a spin-averaged mean-field treatment of the two-electron terms. SPINORBIT experimental use. SPIN_SCAL ON (=1) requests the spin-component scaled variant of the MP2 approach. This keyword has only an effect when CALC_LEVEL=MP2 is specified and must be used together with REF=UHF. SPINROTATION specifies whether nuclear spin-rotation tensors are computed within a NMR chemical
shift calculation (ON, =1) or not (OFF, =9). In the case of electronic g-tensor
calculations for open-shell molecules this keyword controls the calculation of the electronic
spin-rotation tensor. SUBGROUP specifies an Abelian subgroup to be used in a calculation. Acceptable arguments are DEFAULT (=0);
C1 (= 1); C2 (= 2); CS (= 3); CI (= 4); C2V (= 5); C2H (= 6); D2 (= 7) and
D2H (= 8). Use of C1 is of course equivalent to setting SYMMETRY=OFF in
the input. The DEFAULT option (which is the default) uses the highest order
Abelian subgroup. SUBGRPAXIS is a somewhat complicated keyword to use. Allowed values are 0, 1, and 2, which specify the $x$,$y$, and $z$ axes, respectively. The meaning of the keyword is best described by example : Suppose one is running a calculation on water, and wishes to run it in the $C_s$ point group with the ``special plane being the one which bisects the H-O-H bond angle. Now, what SUBGRPAXIS does is to specify which Cartesian direction in the $C_{2v}$ frame becomes the special direction in the $C_s$ frame. CFOUR will orient water in the $yz$ plane, so one wants the $y$ axis in the $C_{2v}$ frame to be the $z$ axis in the $C_s$ frame. Hence, for this case, one would specify SUBGRPAXIS=2. Use of this keyword may be facilitated by studying section D1 of this chapter, entitled ``Molecular Orientation. However, when the true Abelian subgroup is either $C_{2v}$ or $D_{2h}$, the CFOUR orientation is not well defined, and it may be necessary to run the XJODA executable directly two times. If SUBGROUP=0 in the first pass, then the reference orientation for the true Abelian subgroup can be determined and the appropriate value of SUBGRPAXIS selected. SYM_CHECK in principle can be used to force the SCF to converge a solution for which the density matrix transforms as the totally symmetric representation of the point group (i.e. no broken symmetry solutions). The code seems to work in most cases, but has currently been implemented for point groups with E type representation and not for those with triply-, quadruply- or pentuply-degenerate representations. Extending the code to those cases is probably straightforward, and the reader is encouraged to do so if (s)he is so inclined. SYM_CHECK=0 ``forces'' the high-symmetry solution; SYM_CHECK=OVERRIDE (= 1) doesn't. The latter is the default. SYMMETRY specifies what subgroup of the full point group is
to be used in the energy and/or gradient calculation
(The computational point group). OFF (=1)
forces a no symmetry run (in C_1) and ON (=0) runs the calculation
in the largest self-adjoint subgroup (D_2h and its subgroups). T3_EXTRAPOL specifies whether the T3 amplitudes are included (ON, =1) or not included (OFF, =0) in
the DIIS convergence acceleration during CCSDT and higher calculations. Inclusion of T3 speeds up
convergence and allows tight convergence, but on the other hand it increases disk space
requirements. Note that this keyword is only available with modules xecc and xncc T4_EXTRAPOL (not part of the public release) specifies whether the T4 amplitudes are included (ON, =1) or not included (OFF, =0) in
the DIIS convergence acceleration during CCSDTQ calculations. Inclusion of T4 speeds up
convergence and allows tight convergence, but on the other hand it increases disk space
requirements. Note that this keyword is only available with module xncc TAMP_SUM specifies how often the largest t amplitudes are to be printed. =0 Amplitudes are printed at the beginning and end of the run, =1 Amplitudes are printed every iteration, =2 Amplitudes are printed every other iteration, etc. (Default : 5). TDHF experimental use TESTSUITE (currently not available) THERMOCHEMISTRY specifies whether to calculate finite-temperature thermodynamic
corrections after a frequency calculation. OFF (=0) skips
this; ON (=1) gives abbreviated output; and VERBOSE (=2)
gives elaborate output that is separated by translation, rotation and
vibration. TOL_CHOLESKY specifies the threshold to be used in Cholesky decomposition of the two-electron integrals; Cholesky vectors are considered until the
residual is lower than 10$^{-N}$. TRANGRAD experimental use TRANS_INV specifies whether or not translational invariance is exploited in geometrical derivative calculations.
USE(=0) specifies that translational invariance is exploited, while IGNORE (=1) turns it
off. TREAT_PERT specifies whether in a correlated NMR chemical shift calculations all perturbations
are treated at once or sequentially. Available option are SIMULTANEOUS (=0) and
SEQUENTIAL (=1). The latter is at least preferred for large-scale calculations, as
it has less demands on the available disk space. specifies the threshold value
(given as an integer)
for the treatment of CPHF coefficients in second derivative
calculations using perturbed canonical orbitals. If a CPHF coefficient
is above the threshold, the corresponding orbital rotation is treated
(at the expense of additional CPU cost) using the standard non-canonical
procedures, while orbital pairs corresponding to CPHF coefficients below
the threshold are treated using perturbed canonical representation. UNITS specifies the units used for molecular geometry input.
ANGSTROM (= 0) uses Angström units, BOHR (= 1) specifies atomic units. UNOS experimental use UPDATE_HESSIAN specifies whether or not the Hessian update is carried out.
OFF (= 0) uses the initial Hessian (however supplied, either the
default guess or an FCMINT file), ON (= 1) updates it during
subsequent optimization cycles. (not in current public version). experimental use VIBPHASE experimental use VIBRATION specifies whether (harmonic) vibrational frequencies are calculated or not.
If the default NO (=0) is specified then no frequencies are calculated. For
ANALYTIC,
vibrational frequencies are determined from analytically
computed second derivatives, and for FINDIF (=2) vibrational frequencies
are calculated from a force field obtained by numerical differentiation of analytically
evaluated gradients (or even single-point energies) using symmetry-adapted mass-weighted Cartesian
coordinates. If vibrational frequencies
are calculated, a normal mode analysis using the computed force-constant matrix
is performed, rotationally projected frequencies are computed infrared intensities
are determined, and zero-point energies (ZPE) are evaluated. VNATORB This keyword specifies whether virtual natural orbitals are to be used (USE) or not (OFF). (Default : OFF) VTRAN This keyword defines what type of integral transformation is to be performed in the program VTRAN. FULL/PARTIAL (=0) allows the transformation program to choose the appropriate type of transformation, while FULL (=1) requires a full integral transformation and PARTIAL (=2) means an MBPT(2) Specific transformation where the (ab $\vert$ cd) integrals are not formed. functions. (Default : FULL/PARTIAL) specifies the X-component of an external electric
field. The value must be specified as an integer and the field
used by the program will be the value of the keyword {$x10**(-6)$}.
This allows field strengths {$|\varepsilon| > 10^{-6}$} to be used. XFORM_TOL The tolerance for storing transformed integrals. Integrals less than $10^{-N}$ are neglected and not stored on disk. (Default: 11). specifies the Y-component of an external electric
field. The value must be specified as an integer and the field
used by the program will be the value of the keyword {$x10**(-6)$}.
This allows field strengths {$|\varepsilon| > 10^{-6}$} to be used. specifies the Z-component of an external electric
field. The value must be specified as an integer and the field
used by the program will be the value of the keyword {$x10**(-6)$}.
This allows field strengths {$\varepsilon| > 10^{-6}$} to be used. |